Agricultural education trends in digital farming
Digital agriculture tools are fundamentally transforming how agricultural education programs prepare students for modern farming careers. Interactive simulations, remote laboratory access, precision agriculture training platforms, and virtual field experiences now complement traditional hands-on instruction. These technologies enable students to practice complex farm management decisions in risk-free environments, experiment with expensive equipment through virtual interfaces, and access real-time agricultural data from commercial operations. Educational institutions increasingly recognize that graduates must possess both traditional agronomic knowledge and digital competencies to succeed in technology-integrated farming systems that rely on data analytics, automated equipment, and precision management strategies.
Core Digital Agriculture Technologies
Modern agricultural curriculum integrates diverse digital tools that mirror technologies used in commercial farming operations. Students learn GPS-guided equipment operation, analyze satellite imagery for crop health assessment, interpret sensor data streams, and utilize farm management software platforms. These experiences develop technical proficiency while reinforcing scientific principles underlying precision agriculture approaches.
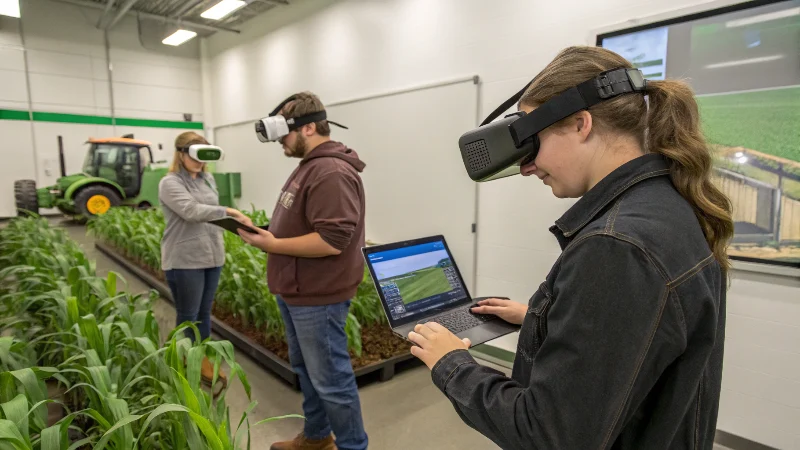
- Virtual reality simulations allow students to practice equipment operation and field scouting without requiring access to expensive machinery or waiting for appropriate growing seasons
- Remote sensing analysis training using actual satellite and drone imagery teaches students to identify crop stress, assess growth stages, and create variable rate application maps
- Cloud-based farm management platforms provide students experience with data integration, record-keeping, and enterprise analysis tools used throughout the agricultural industry
- Sensor network monitoring systems demonstrate real-time decision-making processes, helping students understand how continuous data streams inform irrigation scheduling and pest management interventions

Educational Technology Comparison
The following table compares traditional agricultural education methods with emerging digital approaches, highlighting how technology integration enhances learning outcomes and career preparation.
| Educational Component | Traditional Approach | Digital Agriculture Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Soil Analysis | Laboratory testing with manual equipment | Portable sensors plus spectral analysis software |
| Crop Scouting | Visual field inspection and note-taking | Drone imagery with AI-assisted anomaly detection |
| Equipment Training | Hands-on practice with available machinery | VR simulators plus GPS-guided equipment operation |
| Farm Planning | Paper maps and manual calculations | GIS platforms with integrated data layers and analytics |
"Digital agriculture education prepares students for the data-intensive reality of modern farming. Graduates need fluency in both agronomic science and information technology to optimize increasingly sophisticated production systems."
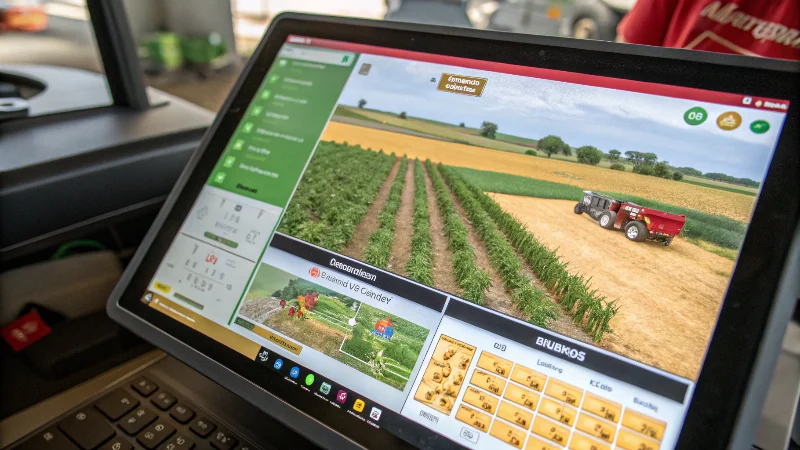
Interactive Field Simulations
Advanced simulation platforms represent perhaps the most transformative digital agriculture education tool, enabling students to manage virtual farms through complete growing seasons while experiencing realistic consequences of their decisions. These systems model weather variability, pest pressure, equipment failures, and market fluctuations, creating authentic learning experiences without financial risks or time constraints of actual production. Students can rapidly iterate management strategies, comparing outcomes across different approaches to develop decision-making skills and systems thinking abilities. As simulation technology improves and incorporates more sophisticated agronomic models, these virtual learning environments will increasingly supplement physical farm laboratories, expanding educational capacity while reducing costs. The integration of digital tools throughout agricultural curriculum ensures graduates possess the technical competencies and analytical mindset required for successful careers in modern, technology-driven farming operations.